How your writing is marked
One of the big mysteries about the FCE exam is how the writing exam is marked. Many of my students ask me about this and, to be honest, it is pretty complex. However, let me break it down for you and let’s go from simple to complex so at the end of the article you will feel more confident and understand what you need to do in order to get great marks in the writing paper.
There are four marking scales in the writing exam. Each of these scales looks at specific aspects of your writing. Generally speaking the four parts are:
- Content – answering the task, supporting your ideas
- Communicative achievement – register, tone, clear ideas, conventions of the specific task type
- Organisation – structure of the text, logical order, connected ideas
- Language – grammar and vocabulary
Each scale is scored out of 5 so you can get a maximum of 20 marks where 3/5 basically means that you have passed this part of your writing.
The four marking scales
Now, of course, it is time to have a look at the four different marking scales in a little bit more detail. I’m going to keep it as simple as possible with examples and explanations so you know what to do.
1. Content
The very first thing an examiner is going to look at is the Content scale. Here they check if you actually answered the task, if you answered it completely and if the reader of the text is fully informed.
So, what exactly does that mean? To find out let’s have a look at an example task from an FCE practice exam.

Looking at the example above there are four different things that we need to include in our writing if we want to score high marks on the Content marking scale.
First of all, there is a question for you to answer and, secondly, there are three topic points that you have to include in this essay. (Yes, your own idea means that you have to write something. Don’t forget this one.) It is also very important that you support your ideas with reasons and examples, which is one thing that separates the average candidates from the great ones. If you want to score high marks, you have to take your writing to a higher level.
To sum this up, always answer all the things that are asked in the task, but don’t stop there. Use reasons and examples to support your ideas to get higher marks and not ‘just pass’.
2. Communicative Achievement
The next marking scale is an interesting one because, in my opinion, it is easy to get good marks here, but at the same time, make mistakes just as easily.
To get high marks in Communicative Achievement you firstly need to show that you understand who is going to read your text. You might think that, of course, it is the examiner, but I’m talking about more of an imaginary reader. Let’s look at two more examples. Who is going to read your text? You got it, your English teacher is the one.

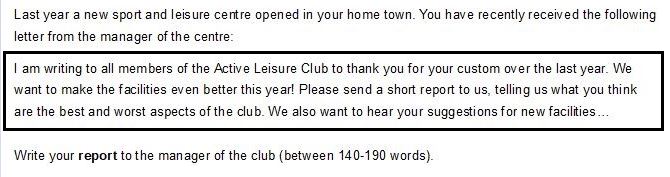
Now the question is what that means for your writing task? Ask yourself what kind of language and tone you would use if you wrote something for your English college magazine or the manager of a leisure centre. Would it be formal or informal? Would you use a lot of slang words and colloquial expressions?
In our first example, we would try to keep it light and rather informal because students are going to be the ones reading it. In the report, on the other hand, we would choose more formal language and stay a little bit more serious than, let’s say, in a review of your favourite film. Make sure that this becomes clear in your choice of grammar and vocabulary as well as some other stylistic features like contractions (I’m vs I am) etc.
Another important point for you to consider is what a report looks like compared to a review? Do you need a title? Subheadings? An introduction and/or conclusion? A greeting and salutation? Think about the specific features of each type of writing and make sure that the text you write looks that way.
Lastly, the Communicative Achievement scale also assesses your ability to clearly express your ideas and to hold the readers attention. You should ask yourself if you would enjoy reading your text and if your arguments or ideas are clearly communicated.
Let’s put this all together before we move on to the next point. Communicative Achievement looks at your ability to use an appropriate style and tone, the correct features for each specific task like title, subheadings, etc. as well as how well you express your ideas and hold the readers attention. It is a lot of stuff, but if you prepare and study these things a little bit, I see no reason why you wouldn’t rock it.
3. Organisation
Organisation, similar to Communicative Achievement, is an area where you can score marks very easily, but a lot of students don’t reach their full potential. We can look at two major problems that students face to explain where candidates lose (or don’t get more) marks.
To begin with, your writing tasks should always be organised in paragraphs. Making paragraphs is an easy task, but there is a little bit more to it than you might think at the beginning.
Looking back at our example from the beginning, how many paragraphs do you think we should use in the essay?

Tough question, I know. When we think about an essay, there should always be an introduction and a conclusion so two paragraphs are already locked in. The task above requires you to write about three topic points: transport, rivers and seas, and your own idea. That’s an additional three paragraphs and a total of five. Do this for every task before you start slamming words onto paper. It will save you a lot of headaches and self-hate.
I often see practice writing tasks that look well organised when I first read them. There are paragraphs clearly separated from each other and I feel a little rush of happiness…until I actually read it and realise that ideas are mixed thoughts are jumping around between different paragraphs and there is no logical order in what my students produce.
However, I don’t blame anyone for doing this because, especially at the beginning of your FCE journey, you simply don’t know what is expected of you.
So, paragraphs are great, but you have to put them in logical order (which depends on the task you’re working on) and have one main idea per paragraph. Don’t try to cram five different things in one. Make a plan before you start writing and avoid these unnecessary mistake.
Secondly, the examiner looks at your ability to connect your ideas using linking words and other methods. Once again, these words and methods can be similar for some task types but different for others.
Organisation checks your ability to bring a logical order to your writing. Use paragraphs for your main ideas and connect everything with linking words and other useful language. Make a plan and get organised before you start writing, save yourself some time and avoid getting stressed out.
4. Language
Language is probably the one marking scale that is quite straight forward. You are assessed on your use of grammar and vocabulary, which includes if you make a lot of errors as well as how wide your range of grammar and vocabulary is.
For example, if you are writing about travelling you should show a wide range of vocabulary specific to this topic. For a task about the environment the vocabulary changes. I guess that makes sense. The more pointed towards the task your words and expressions are, the better it is for your marks.
In the grammar department it is not so much about the task, but rather about you trying to use structures that are outside of your comfort zone or not. You don’t have to be perfect at this level of English so the FCE examiners recognise even attempts at more complex grammar.
So, the next time you practise writing for the exam challenge yourself to use at least three grammatical structures that you find difficult, such as conditionals, the passive voice or reporting verbs. Again, in the exam you won’t get punished for trying so why not try?
Writing is not as bad as it seems
After all this information you might feel a little overwhelmed wondering how you can meet all these requirements and get high marks. The good thing is that you really don’t need to worry too much. I know that you already do a lot of the points discussed in this post well. Your job is now to find the areas in which you can improve and start to work on them. All you need to do is trust yourself (and Teacher Phill).
I hope this article helps you understand better how the writing exam works and, more importantly, what happens after you finish the exam. As always, don’t wait until it’s too late. Tackle your problems now and you will improve. If you start today, I’m sure there won’t be a problem once you are in the examination room and your pen is going to fly over the paper.
Lots of love,
Teacher Phill 🙂








Thanks! Very clear examples.
Hi Anne,
Thank you for your feedback and I’m happy you find my article useful. 🙂